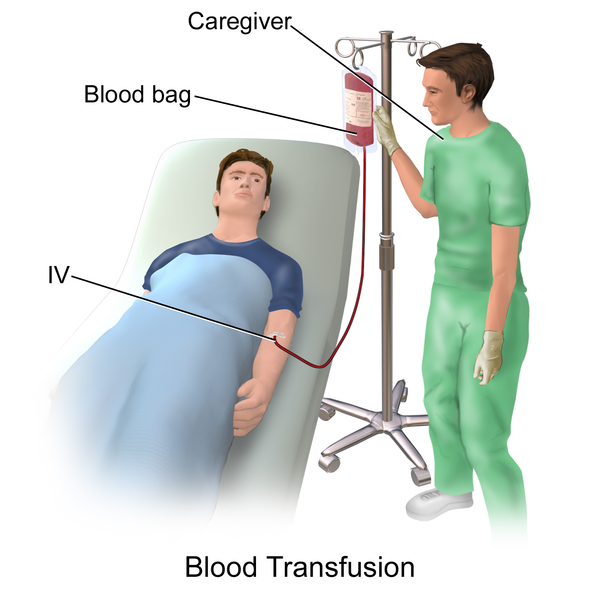
A blood transfusion is a procedure in which a person receives blood from a different person. The donor’s blood is stored in special bags. During the procedure, the healthcare provider connects the needed bag to an intravenous line (a tubing that goes into the veins). Then, the healthcare provider inserts a needle into the vein, and the blood starts to circulate through the body. The healthcare provider will check the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and type of blood. The blood is checked for clotting and infection. The patient’s name should be on the bags and the patient should return to the hospital 15 minutes later.
The healthcare provider will collect the blood from a vein in the patient. The blood may be screened using antigens in the blood. If the patient has antigens in the blood, the body will recognize it. The patient’s body will react to this foreign blood by producing antibodies that attack the foreign blood. This reaction is called a transfusion reaction. It should be rare, but it’s important to note that allergic reactions can happen during a transfusion.
Immune-related reactions are possible complications of blood transfusion. A patient’s immune system may react to a transfused blood component and cause an allergic reaction. These reactions are not life-threatening if treated promptly. The most common side effects of a transfusion are itching, hives, wheezing, and fever. It’s also important to note that a patient’s body can’t tell if a transfusion reaction is allergic.
Some patients may be afraid of blood transfusions. The health worker will make sure that the blood transfusion is safe. They will carefully screen donors and use the correct blood type. When people need it, transfusions work well. If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider will be able to answer any questions you may have. Better to be safe than sorry later.
Before a blood transfusion, a blood sample is taken from the patient. The blood is tested to determine if the patient has the same blood type as the transfused blood. The patient is safe only if the blood belongs to the same group as his own. The blood transfusion takes 2 to 4 hours. However, in most cases, the patient will feel better within a few hours after the procedure.
The most common risks of blood transfusions are allergic reactions and fever. This reaction is usually not serious, but can be dangerous if it occurs within a few hours. Other side effects include nausea and chest pain. An allergic reaction to the blood is also possible. In the event of an allergic reaction, you should not hesitate to contact your healthcare provider and visit the health website iHealzy Thailand. They will help you choose the best blood type for you.
A blood transfusion can be dangerous, but it is necessary for your health. You must follow the recommendations given by your healthcare provider. In addition to risk prevention, make sure you’re getting the right blood for your body type. You should ask your healthcare provider if you should be concerned about the risks associated with the procedure. It is important to be prepared to transfuse. You must be a good candidate for a healthy blood transfusion.
Blood transfusion can cause fever. Fortunately, this is rare. In most cases, transfusion can lead to positive reactions. Some patients may experience temporary fever, but the symptoms may be life-threatening. The patient should also be in a comfortable position, as this can make them more sensitive to blood. Therefore, before a blood transfusion, make sure your doctor is aware of your medical history.
A blood transfusion can cause some unpleasant symptoms. The area where the drip was placed may be sore for several hours. Contact your health care provider if you experience any of these symptoms. In some cases, it may be necessary to stop the transfusion for a few days to make sure you are all right. This process can be a life-saving procedure, but it can also be dangerous. Although there is no guarantee, it is important to understand all the risks and complications.