This chapter gives a general overview of bone biology. The chapters are divided into three sections: basic structure, mechanical properties, and adaptation to pathological conditions. In this chapter, you will learn about the origin of bone and the functions of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoblast-like cells. They are the keystones of the skeletal system and are responsible for the development of bones. However, this review of bone function should not be confused with the anatomy of the skeleton.
The most important part of a study of bone is the understanding of the underlying mechanisms. The function of bone is to support the body’s structure, protect the vital organs, and store ions. In addition, it is a reservoir for ions. After growth and modeling of the skeleton, it undergoes constant remodeling to meet the demands of changing functions. As with any other material, it is made up of various types of cells, including collagenous extracellular organic matrix (ECOM), and mineral content.
In terms of mechanical behavior, bone is subjected to a variety of nonhabitual and abnormal situations. Experiments are used to measure the strength and stiffness of bone tissue. In addition to being important for the understanding of the function of bone, it is also important to know the anatomy of bone tissues. In skeletal engineering, the shape of a specimen can be very critical to its performance. For example, the scapula is a bone with a superior angle and inferior angles.
Another important part of studying the mechanical behavior of bone is its ability to withstand mechanical stress. Experiment is a way to find out if bone tissue can withstand such demands. A well-designed experiment is an important tool for determining the ability of a fabric to withstand these forces. To do this, the sample must have the correct geometry. The applied load is usually expressed in terms of force, stress or strain.
The structure of the bone is characterized by its unevenness. In addition to these disorders, the structure of the bone is also complex. It is made up of different types of cells. For example, a branch is a curved part of a bone that provides structural support to the rest of the bone. This is referred to as a notch in the bone model. The branch of the lower jaw has a notch at the base of the articular bone.
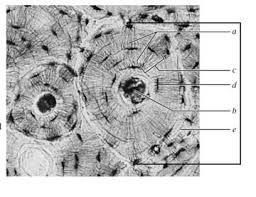
In addition to the skeletal system, the bone is also an active organ. Destructive and building processes are constantly taking place in it. The contours of the bone reflect the forces it faces. The contours of the bones are formed by the articular surfaces between the bones. They form a rigid structure that supports the weight of the body. The articulating surface between two bones is where the two surfaces are developed. These structures are called the "articulating" elements of the bone.
During the evolution of bones, it was found that bones contain specialized connective tissue that forms a rigid endoskeleton. The structure of the bone is very dynamic and changes at different stages of development. The processes of its growth and modeling are responsible for the evolution of the skeletal system. It is important to understand the mechanism of bone tissue in order to develop an effective treatment. If you are looking for trauma treatment, this should be the most appropriate type of rehabilitation for the patient.
Since bone is an elastic material, it experiences various types of stresses and deformations. For example, a fracture can lead to fractures. A patient with broken bones must undergo surgery to repair them. Alternatively, the patient may undergo a procedure in which the bone is broken. In both cases, the osteo-papillary ligament will be reconstructed. It is important that the person has the proper treatment. The health site Club Salamanca describes that the osteo-papillary fibers of the skeletal system must be inserted to prevent further damage to the body.
Cortical bone is made up of various types of cells that play an important role in maintaining its shape and function. One type of bone tissue is compact, dense and hard. On the other hand, spongy bones are soft and pliable. Moreover, human bones differ in their density, so both the body and the joints are different. It is important to note that the two types of cells in bone are closely related, and three types contribute to bone homeostasis.